Industry Thought Leadership
Satisfy 5G Data Transmission Capacity Demand With a New-generation Fiber
June, 20205G communication is clearly a leading trend in the telecom industry today. This new reality of connecting all and everything is in the air – but not only there. 5G mobile communication is expected to support the transmission of much larger volumes of data with much lower signal latency than the former generation. This imposes extreme requirements in terms of transmission capacity on the wireline part of the transport network – the telecom grid critical for supplying each 5G radio-base-station or antenna mast. This grid functions using millions of kilometres of optical fiber cables that have to support both the ongoing incremental increases in transmission requirements as well as extreme peak demands like that recently caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The most obvious way to increase the capacity of optical fiber systems is to deploy cables with higher fiber counts. However, a less evident problem emerges, especially in highly dense urban areas: the existing infrastructure is not capable of accommodating a larger number of optical fiber cables. There are two main reasons for this. Firstly, the capacity of cable ducts is limited, resulting in massive cost increases for new cable installations; and secondly, optical fiber telecom systems need to follow the trend towards miniaturization and integration in current technology.
There remains only one efficient, unexplored dimension for increasing fiber capacity, and that is adding more spatial channels in a single fiber strand. Each such channel – or core – shall perform as a single-core fiber in terms of transmission properties and be fully compliant with legacy fiber installations and active equipment.
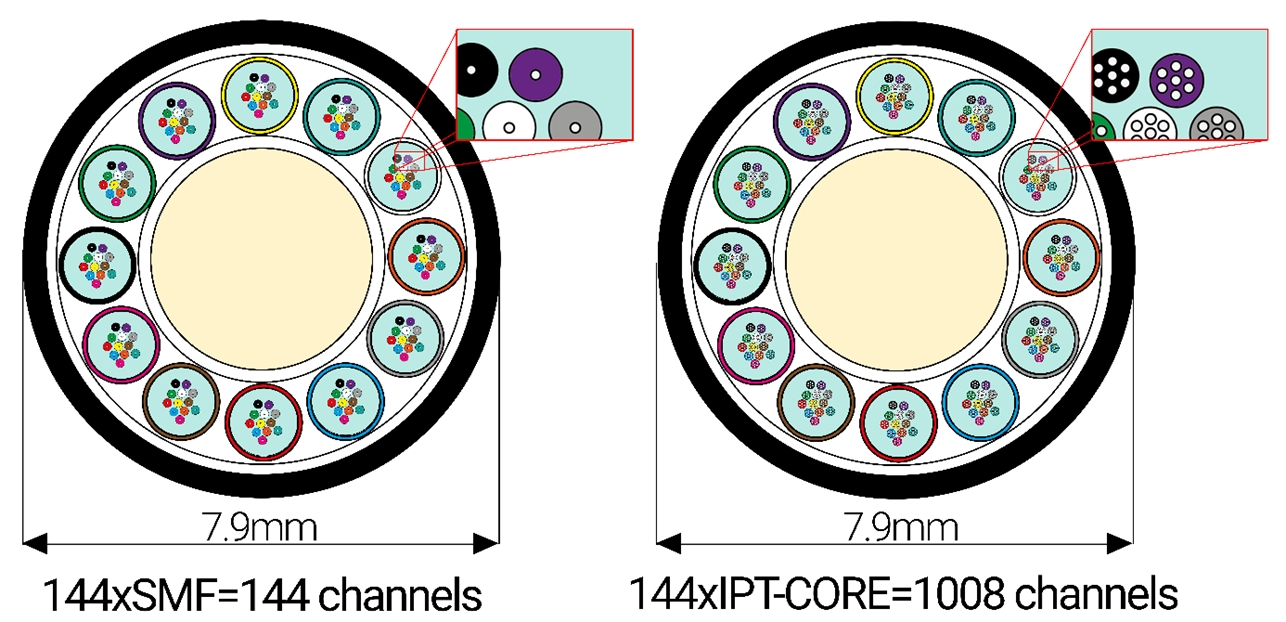
IPT-CORE multicore fibers by InPhoTech are an innovative solution dedicated to boosting optical link capacity. These standard diameter fibers contain 7 separated cores (with 19-cores available in an increased-diameter fiber). In InPhoTech’s proprietary design each single-mode core of IPT-CORE is fully compliant with the ITU-T G.652 recommendation so that other established signal multiplexing methods can be used effectively. As a result the transmission capacity within a single optical fiber cable multiples dramatically.
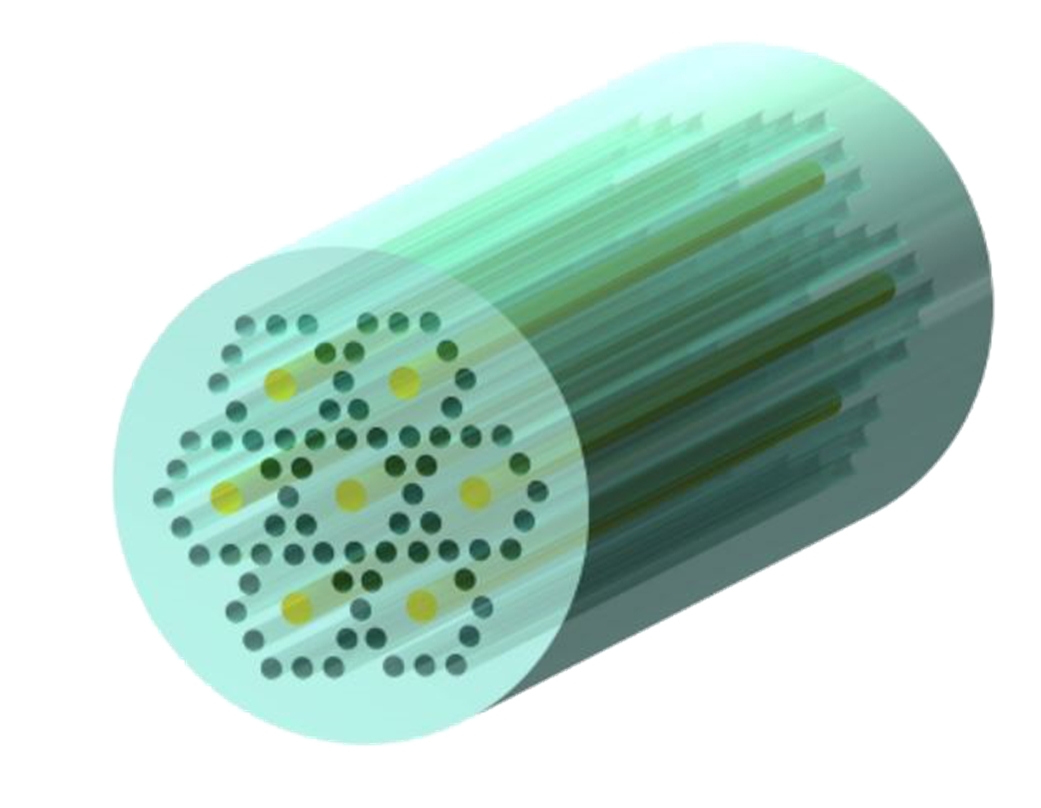
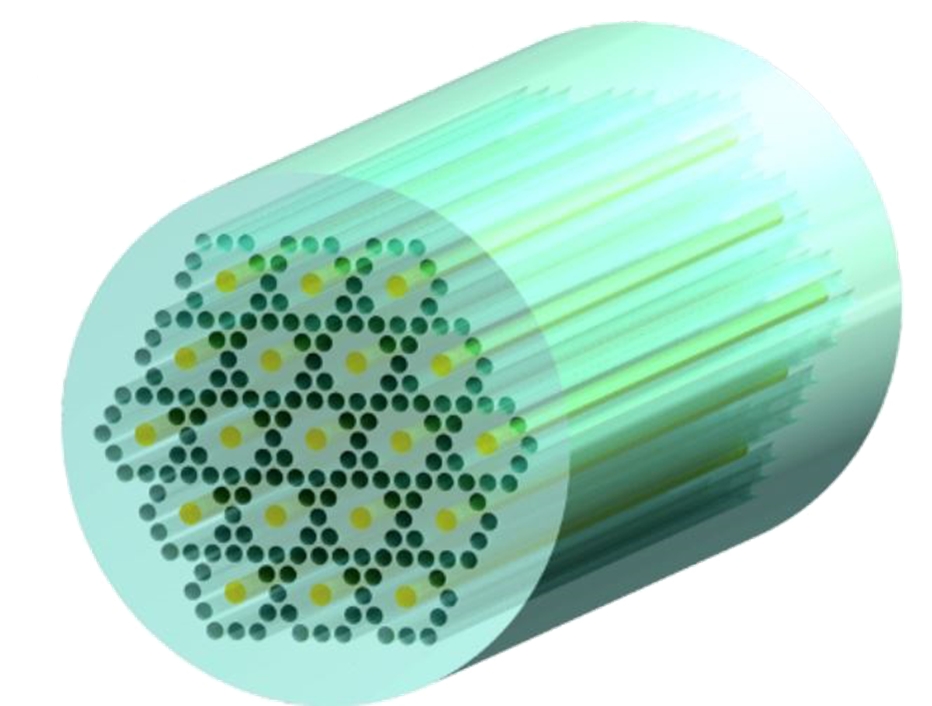
In order to allow multicore fibers to be deployed quickly and easily for industrial application, InPhoTech has created a fiber design ready for implementation in existing networks. A complete system based on InPhoTech’s IPT-CORE consists of a 7-core or a 19-core passive optical fiber together with fan-in/fan-out components on both ends of the fiber. The fan-in/fan-out component allows information to be sent and received to and from each core independently, thus effectively providing the functionality of 7 or 19 fibers within a single fiber. Furthermore, 1x7 all-fiber power splitters and erbium doped active multicore fibers (an active IPT-CORE) for signal amplification are also available. These products enable InPhoTech’s solution to be used in long-haul, metro or access networks without replacing the existing transmitting-receiving devices.
Besides the necessary technological developments, there are solid economic reasons for turning towards IPT-CORE fibers. In terms of network deployment and maintenance, multicore fiber is expected to bring savings of 70% to 80% in investment and operational expenditures respectively. This comes from the reduced number of fibers to be installed, lighter cabling, fewer fiber terminations, less space occupied in a telecom duct and shorter time-to-repair.
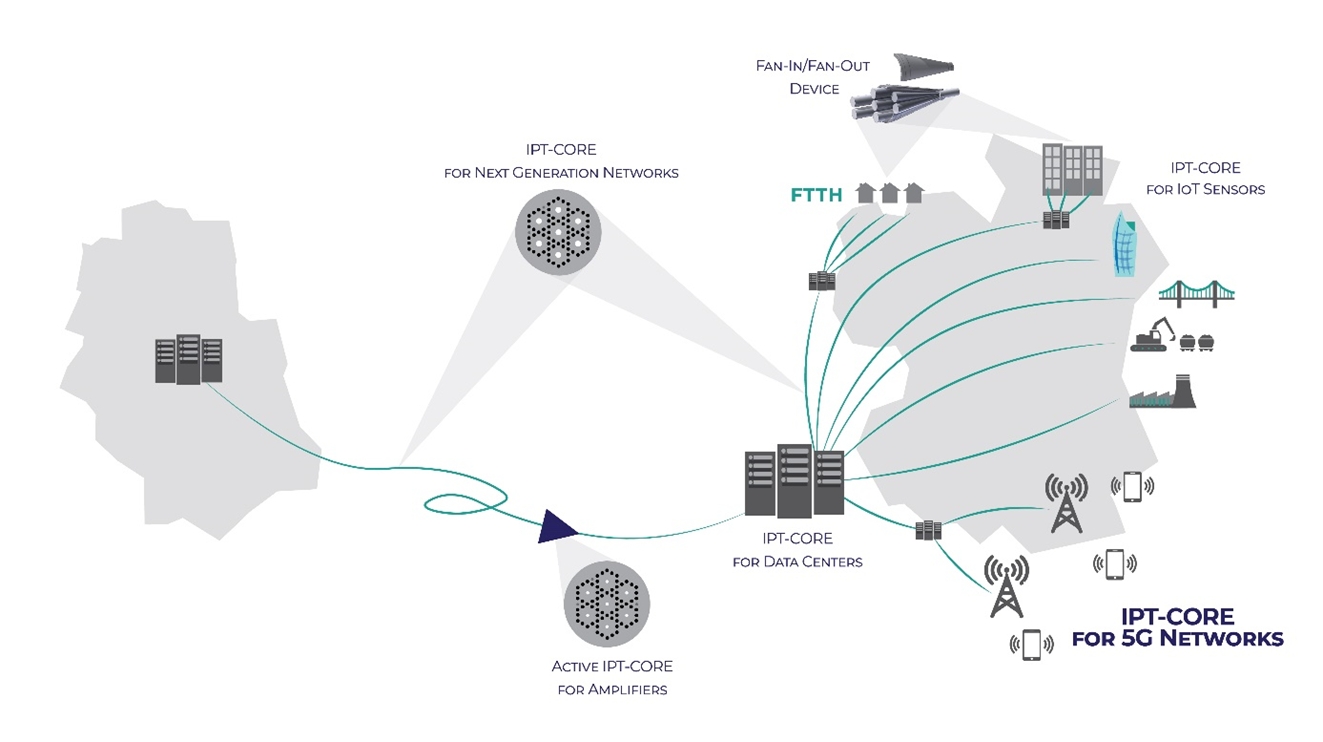
Providing a complete solution, the IPT-CORE technology by InPhoTech satisfies the demand for increased capacity in telecom networks, making it both available and affordable. IPT-CORE is ready to fit a multiplied transmission into an existing infrastructural envelope. Designed with network integration in mind our multicore fibers and components enable quick deployment and provide an efficient investment in next-generation network capacity.

